Characteristics
 The great kiskadee is a large member of the flycatcher family. It is about ten inches in length.It has black and white stripes on the crown and sides of its head. The great kiskadee is a large member of the flycatcher family. It is about ten inches in length.It has black and white stripes on the crown and sides of its head.
It has a white line above its eyes. Its chest and undersides are a bright yellow and its throat is white. Its back and wings are brown and its bill and legs are black.
Range
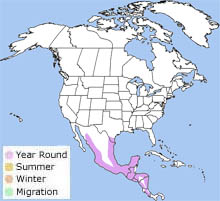 The great kiskadee is found from extreme southern Texas south to Argentina. The great kiskadee is found from extreme southern Texas south to Argentina.
|
|
Habitat
The great kiskadee lives in open woodlands, streamside thickets, groves, orchards and parks.
Diet
 The great kiskadee eats insects like beetles, wasps, grasshoppers, bees and moths. Despite the fact that it is a flycatcher, it also eats berries, seeds, mice, frogs, fish and lizards. It also will dive straight into the water to catch fish. The great kiskadee eats insects like beetles, wasps, grasshoppers, bees and moths. Despite the fact that it is a flycatcher, it also eats berries, seeds, mice, frogs, fish and lizards. It also will dive straight into the water to catch fish.
Life Cycle
 Kiskadees are monogamous. A male will mate with only one female. Mating season begins in late March. The female great kiskadee lays two to five creamy-white and brown speckled eggs in a domed nest made of sticks, grass, moss and bark. The nest has a single entry hole and is lined with soft material like wool and feathers. The nest is usually built in a thorn tree or bush. Both parents defend the nesting territory and care for the young. Kiskadees are monogamous. A male will mate with only one female. Mating season begins in late March. The female great kiskadee lays two to five creamy-white and brown speckled eggs in a domed nest made of sticks, grass, moss and bark. The nest has a single entry hole and is lined with soft material like wool and feathers. The nest is usually built in a thorn tree or bush. Both parents defend the nesting territory and care for the young.
Behavior
 The great kiskadee is named for its loud "kis-ka-dee" call. It travels in pairs and aggressively protects its nesting territory. One of its most feared predators is the coral snake and the kiskadee will stay away from anything that has the same color pattern as the coral snake. The great kiskadee is named for its loud "kis-ka-dee" call. It travels in pairs and aggressively protects its nesting territory. One of its most feared predators is the coral snake and the kiskadee will stay away from anything that has the same color pattern as the coral snake.
|