Characteristics
 The American black duck is not really black, it is more of a dusky brown, In fact, it is sometimes called the dusky duck. It is 19-22 inches in length. Its neck and head are a lighter color than its body. Its bill is olive-yellow to orange, and its wings have a purplish-blue patch and are white on the underside. Males and females look alike, although the female is a little lighter. The American black duck is not really black, it is more of a dusky brown, In fact, it is sometimes called the dusky duck. It is 19-22 inches in length. Its neck and head are a lighter color than its body. Its bill is olive-yellow to orange, and its wings have a purplish-blue patch and are white on the underside. Males and females look alike, although the female is a little lighter.
Range
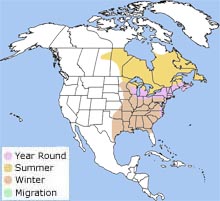 The American black duck breeds in eastern and central North America from Manitoba and Labrador to Texas and Florida. It winters from southern Minnesota and Nova Scotia south to southern Texas and central Florida. Inbreeding between American black ducks and mallards, along with habitat loss and competition with the mallard for resources, has led to a decrease in the number of American black ducks in the last 40 years. In areas where there is a lot of hunting and fishing, lead poisoning from shot and fishing tackle has poisoned many American black ducks. The American black duck breeds in eastern and central North America from Manitoba and Labrador to Texas and Florida. It winters from southern Minnesota and Nova Scotia south to southern Texas and central Florida. Inbreeding between American black ducks and mallards, along with habitat loss and competition with the mallard for resources, has led to a decrease in the number of American black ducks in the last 40 years. In areas where there is a lot of hunting and fishing, lead poisoning from shot and fishing tackle has poisoned many American black ducks.
Habitat
The American black duck can be found in marshes, lakes, ponds, swamps, streams, coastal mudflats and estuaries.
Diet
 The American black duck feeds in shallow water. It tips its head down and lifts its tail up so it can probe or dabble in the mud and water for submerged plants and seeds. It also eats mollusks, crustaceans, insect larvae, tadpoles, small fish and frogs. It sometimes skims the surface of the water for seeds and aquatic invertebrates. The American black duck feeds in shallow water. It tips its head down and lifts its tail up so it can probe or dabble in the mud and water for submerged plants and seeds. It also eats mollusks, crustaceans, insect larvae, tadpoles, small fish and frogs. It sometimes skims the surface of the water for seeds and aquatic invertebrates. | |
|
Life Cycle
 Breeding begins in March to May, depending on latitude. The female selects a nest site in a clump of grass, under a shrub or tree or in a fork or hole in a tree. The male will defend the territory while the female builds the nest. In ground nests, she digs a scrape with her bill and feet and lines it with grass, feathers and other plant materials. She also plucks down from her body and lines the nest with it. She lays 7-17 eggs. When the female has to leave the nest, she will cover the eggs with down to keep them warm.
 The male will stay near the nest but doesn't incubate the eggs. He will leave as the incubation period draws to a close. He will then fly to an isolated area to molt.
 The chicks hatch in about 29 days and shortly after hatching the female will lead them to water. The ducklings will eat mosquito larvae and other aquatic invertebrates from the water's surface for the first couple of weeks. As they get older, they will begin eating tadpoles and snails. Eventually, they will start dabbling under the water for seeds, tubers and aquatic plants. The female will stay with the ducklings for seven to eight weeks until their flight feathers come in. She then leaves the ducklings and begins her molt.
Behavior
 Like other dabbling ducks, the American black duck takes off straight from the water to fly. Diving ducks have to run across the water to get up enough speed to launch themselves into flight.
|