Characteristics
 The Canada goose has a long black neck and head with a white band on its cheeks that runs under its chin like a strap. It has black feet and a light tan body with lighter brown or white under its tail. The Canada goose has a long black neck and head with a white band on its cheeks that runs under its chin like a strap. It has black feet and a light tan body with lighter brown or white under its tail.
 Its black bill has lamellae, or teeth, around the outside edges that are used as a cutting tool.
Males and females look alike, although females are usually a little smaller than the males. Its black bill has lamellae, or teeth, around the outside edges that are used as a cutting tool.
Males and females look alike, although females are usually a little smaller than the males.
Range
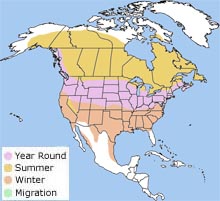 The Canada goose breeds and winters in most of Canada and the United States. The Canada goose breeds and winters in most of Canada and the United States.
Habitat
The Canada goose can be found in a wide variety of habitats including lakes, bays, rivers and marshes. It often feeds in open fields and grasslands.
Diet
On land, the Canada goose eats a wide variety of grasses, including salt grass and Bermuda grass. It uses its bill to yank the grass out of the ground. It also eats corn, rice and wheat. In the water, the Canada goose sticks its head and upper body under the water, stretches its neck out and uses its bill to scoop up food from the mud and silt. |
|
Life Cycle
The female Canada goose lays her eggs between March and June. She will lay between four to ten whitish eggs in a nest made of grass, reeds and moss and lined with down. The nests are usually on the ground near water. The female hatches the eggs and turns them over often to evenly heat them.
The male will guard the female and the nest and will call out a warning if danger approaches. It takes about a month for the eggs to hatch. The chicks break out of the shell with an egg tooth on the top of their bills. It may take them one to two days to completely break out of the shell. The chicks will fly when they are between 40 and 70 days old. Most Canada geese will mate for life.
Behavior
 Canada geese migrate in large V-shaped formations. They honk loudly while they are flying. They migrate at a slow pace. Male Canada geese can be very aggressive they will often attack predators with their wings and bill.
|