Characteristics
 The greater roadrunner is a member of the cuckoo family. It is a ground bird that is about two feet in length. It has speckled brown and black feathers on its back and wings and a lighter throat and chest with dark stripes. It has long legs, a very long tail and yellow eyes. It has a crest on its head and the male has a red and blue patch of skin on the side of its head. The greater roadrunner is a member of the cuckoo family. It is a ground bird that is about two feet in length. It has speckled brown and black feathers on its back and wings and a lighter throat and chest with dark stripes. It has long legs, a very long tail and yellow eyes. It has a crest on its head and the male has a red and blue patch of skin on the side of its head.
Range
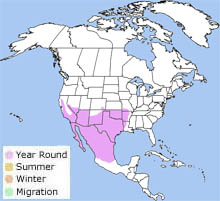 The greater roadrunner can be found in Arizona, California, Nevada, New Mexico, Utah, Colorado, Kansas, Oklahoma, Arkansas, and Louisiana. It is also found in Mexico. The greater roadrunner can be found in Arizona, California, Nevada, New Mexico, Utah, Colorado, Kansas, Oklahoma, Arkansas, and Louisiana. It is also found in Mexico.
Habitat
 The greater roadrunner is most common in desert areas, but it can also be found in chaparral, grasslands, open woodlands and agricultural areas. The greater roadrunner is most common in desert areas, but it can also be found in chaparral, grasslands, open woodlands and agricultural areas.
|
|
Diet
 The greater roadrunner eats small snakes, lizards, mice, scorpions, spiders, ground nesting birds and insects. It also eats fruits and seeds. The greater roadrunner eats small snakes, lizards, mice, scorpions, spiders, ground nesting birds and insects. It also eats fruits and seeds.
Life Cycle
 The female lays three to six eggs in a stick nest lined with grass. The nest is usually placed in a low tree, bush, thicket or cactus 3-15 feet above the ground. Males do most of the incubating because they keep a normal body temperature at night. The female's body temperature drops at night. The female lays three to six eggs in a stick nest lined with grass. The nest is usually placed in a low tree, bush, thicket or cactus 3-15 feet above the ground. Males do most of the incubating because they keep a normal body temperature at night. The female's body temperature drops at night.
If a predator comes too close to the nest, the male will run in a crouch until he is a short distance away from the nest. He then will stand up, raise and lower the crest on his head, flash the blue and red patches on the sides of his head and call out in an attempt to lure the predator away from the nest.
The chicks hatch in about 20 days. Both parents care for the young. The chicks leave the nest when they are 18 days old and can feed themselves when they are 21 days old.
Behavior
 The roadrunner gets its name from its great running ability. When it is startled it will run rather than fly. It is a poor flyer but can run at speeds of up to 15 miles per hour. It uses its long tail as a type of rudder to help it keep its balance while running. The roadrunner gets its name from its great running ability. When it is startled it will run rather than fly. It is a poor flyer but can run at speeds of up to 15 miles per hour. It uses its long tail as a type of rudder to help it keep its balance while running.
|