Characteristics
 The little blue heron is a small heron. It is about two feet tall with a wingspan of about 40 inches. It has slate-blue feathers with a maroon neck and head. Its bill is gray with a black tip, and it has gray to blue legs and feet. Males and females look alike. The little blue heron is a small heron. It is about two feet tall with a wingspan of about 40 inches. It has slate-blue feathers with a maroon neck and head. Its bill is gray with a black tip, and it has gray to blue legs and feet. Males and females look alike.
 Young little blue herons are white and have blue bills with a black tip and dull green legs. When immature little blue herons are molting into their adult plummage, they can be a mix of white and blue. Young little blue herons are white and have blue bills with a black tip and dull green legs. When immature little blue herons are molting into their adult plummage, they can be a mix of white and blue.
Range
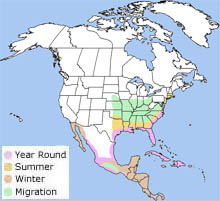 The little blue heron breeds from New England south to Florida, Mexico, and the Caribbean. It also breeds in the southern United States and the Gulf Coast. Occasionally, it breeds in Southern California and New Mexico. It winters on the Gulf Coast and on the Atlantic Coast north to New Jersey. The little blue heron is also found in the tropics. The little blue heron breeds from New England south to Florida, Mexico, and the Caribbean. It also breeds in the southern United States and the Gulf Coast. Occasionally, it breeds in Southern California and New Mexico. It winters on the Gulf Coast and on the Atlantic Coast north to New Jersey. The little blue heron is also found in the tropics.
Habitat
 The little blue heron makes its home in freshwater swamps, lagoons, coastal thickets and islands. The little blue heron makes its home in freshwater swamps, lagoons, coastal thickets and islands.
|
|
Diet
 The little blue heron eats fish, crustaceans, amphibians, insects and reptiles. It stands in shallow water and waits for its prey to go by, and then it grabs its prey with its pointed bill. The little blue heron eats fish, crustaceans, amphibians, insects and reptiles. It stands in shallow water and waits for its prey to go by, and then it grabs its prey with its pointed bill.
Life Cycle
 The male usually chooses the nesting territory before selecting a female. The male courts the female by stretching his neck out and pointing his bill up in the air. He then crouches and may snap his bill, sway his neck from side-to-side, and vocalize. The female may approach him aggressively at first, but soon the pair groom each other and twine their necks together. The male usually chooses the nesting territory before selecting a female. The male courts the female by stretching his neck out and pointing his bill up in the air. He then crouches and may snap his bill, sway his neck from side-to-side, and vocalize. The female may approach him aggressively at first, but soon the pair groom each other and twine their necks together.
 The male then gathers twigs for the nest and presents them to the female, who builds the nest. The nest is made of sticks, reeds, and grass. The nest is usually built a few feet above the ground in a tree or a bush, although sometimes it is built on reeds or on the ground. The female lays 3-5 eggs. The eggs hatch in about three weeks. Both parents incubate the eggs. Chicks are fed regurgitated food by both parents. They fledge when they are 35-40 days old. The little blue heron has a life span of up to seven years. The male then gathers twigs for the nest and presents them to the female, who builds the nest. The nest is made of sticks, reeds, and grass. The nest is usually built a few feet above the ground in a tree or a bush, although sometimes it is built on reeds or on the ground. The female lays 3-5 eggs. The eggs hatch in about three weeks. Both parents incubate the eggs. Chicks are fed regurgitated food by both parents. They fledge when they are 35-40 days old. The little blue heron has a life span of up to seven years.
Behavior
The little blue heron often follows farmers as they are plowing fields and then grabs the insects that are disturbed by the plow.
|