Characteristics
 The moose is the largest member of the deer family and the tallest mammal in North America. It stands six feet tall from shoulders to feet. Females weigh between 800 to 1,300 pounds
and males
weigh 1,200 to 1,600 pounds. The moose is the largest member of the deer family and the tallest mammal in North America. It stands six feet tall from shoulders to feet. Females weigh between 800 to 1,300 pounds
and males
weigh 1,200 to 1,600 pounds.
 The moose has long, thick, light brown to dark brown fur. Moose hair is hollow, which helps keep the moose warm. The moose has long legs. Its front legs are longer than its rear legs. This helps it jump over fallen trees and other forest debris. It has a long head with a large nose and upper lip. It has small ears, a small tail, and a dewlap hanging on its throat. It has powerful shoulder muscles that give it a humpbacked appearance. The moose has long, thick, light brown to dark brown fur. Moose hair is hollow, which helps keep the moose warm. The moose has long legs. Its front legs are longer than its rear legs. This helps it jump over fallen trees and other forest debris. It has a long head with a large nose and upper lip. It has small ears, a small tail, and a dewlap hanging on its throat. It has powerful shoulder muscles that give it a humpbacked appearance.
 The male or bull moose has huge broad and flat antlers that can stretch 4 to 5 feet across. Antlers start to grow in the early summer. When antlers first start to grow, they are covered with a soft fuzzy skin called velvet. The velvet has blood vessels in it that deliver nutrients that help the antlers grow. By late summer, when the antlers reach full size, the blood supply dries up and the velvet starts to drop off.
In Europe the moose is known as the elk. The male or bull moose has huge broad and flat antlers that can stretch 4 to 5 feet across. Antlers start to grow in the early summer. When antlers first start to grow, they are covered with a soft fuzzy skin called velvet. The velvet has blood vessels in it that deliver nutrients that help the antlers grow. By late summer, when the antlers reach full size, the blood supply dries up and the velvet starts to drop off.
In Europe the moose is known as the elk.
Range
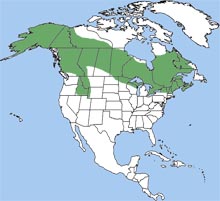 In North America, the moose is found in Alaska, Canada, the northeastern United States, and as far south as the Rocky Mountains in Colorado. A close relative of the moose, the Eurasian Elk (Alces americanus) is found in northern Europe and Asia. In North America, the moose is found in Alaska, Canada, the northeastern United States, and as far south as the Rocky Mountains in Colorado. A close relative of the moose, the Eurasian Elk (Alces americanus) is found in northern Europe and Asia.
Habitat
 The moose lives in forested areas where there is snow cover in the winter and nearby lakes, bogs, swamps, streams and ponds.
The moose's large size makes survival in warm climates difficult, and they have difficulty when temperatures rise above 80 degrees Fahrenheit. In the summer, they cool off in the water. The moose lives in forested areas where there is snow cover in the winter and nearby lakes, bogs, swamps, streams and ponds.
The moose's large size makes survival in warm climates difficult, and they have difficulty when temperatures rise above 80 degrees Fahrenheit. In the summer, they cool off in the water.
|
|
Diet
 Moose is an Algonquin term for "twig eater." The moose is a browser. In warm months it eats the leaves, twigs and buds of hardwood and softwood trees and shrubs. It also feeds on aquatic plants like water lilies. In the winter the moose browses on woody plants like the twigs and bark of willow, balsam, birch, aspen and dogwood trees. Moose is an Algonquin term for "twig eater." The moose is a browser. In warm months it eats the leaves, twigs and buds of hardwood and softwood trees and shrubs. It also feeds on aquatic plants like water lilies. In the winter the moose browses on woody plants like the twigs and bark of willow, balsam, birch, aspen and dogwood trees.
Life Cycle
 Moose mate in early fall. During mating season, females attract males with their deep calls and strong scent. Bull moose use their antlers in threat displays when they are fighting over females. Sometimes they will get into a pushing fight with their antlers. These fights rarely get too serious because the antlers could catch together and both moose could die. Moose mate in early fall. During mating season, females attract males with their deep calls and strong scent. Bull moose use their antlers in threat displays when they are fighting over females. Sometimes they will get into a pushing fight with their antlers. These fights rarely get too serious because the antlers could catch together and both moose could die.
When mating season is over, the moose's antlers will fall off. Mice and other rodents will gnaw on the antlers because they are a good source of calcium.
 The female gives birth during the spring or summer. She usually has one baby. Moose calves can stand up within a day, and they can swim within a couple of weeks. The female gives birth during the spring or summer. She usually has one baby. Moose calves can stand up within a day, and they can swim within a couple of weeks.
 Calves are weaned after about six months and will stay with their mother until the next young are born. Mothers are very protective of their calves and will charge people if they get too close. Bull moose may also charge people and even cars during mating season. Moose can run as fast as 35 mph, so it's a good idea to stay out of their way! Calves are weaned after about six months and will stay with their mother until the next young are born. Mothers are very protective of their calves and will charge people if they get too close. Bull moose may also charge people and even cars during mating season. Moose can run as fast as 35 mph, so it's a good idea to stay out of their way!
Behavior
 The moose is active in the day, especially at dawn and dusk. It has very poor eyesight but good hearing and an excellent sense of smell. It is a very good swimmer and can swim as fast as six miles an hour in the water. The moose is usually a peaceful animal but can become aggressive when it is threatened. It is never a good idea to approach a moose. Moose are very territorial, and if they think you are a threat, they will charge at you. Moose are faster than humans, so you can't outrun one! The moose is active in the day, especially at dawn and dusk. It has very poor eyesight but good hearing and an excellent sense of smell. It is a very good swimmer and can swim as fast as six miles an hour in the water. The moose is usually a peaceful animal but can become aggressive when it is threatened. It is never a good idea to approach a moose. Moose are very territorial, and if they think you are a threat, they will charge at you. Moose are faster than humans, so you can't outrun one! |