Characteristics
 The pied-billed grebe is 9-15 inches in length with a wingspan of 16-24 inches. It has a small, stocky body; a long neck; and a rounded head. It is brown over most of its body and has a white rump. It has a short, stubby whitish bill. Its bill has a dark ring around it during breeding season.
Males and females look the same. The pied-billed grebe is 9-15 inches in length with a wingspan of 16-24 inches. It has a small, stocky body; a long neck; and a rounded head. It is brown over most of its body and has a white rump. It has a short, stubby whitish bill. Its bill has a dark ring around it during breeding season.
Males and females look the same.
Range
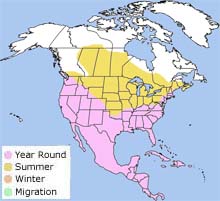 The pied-billed grebe's range covers most of eastern and central Canada and all of the United States. In the northern parts of its range, the pied-billed grebe will migrate to areas with open water. It will live year-round In the southern part of its range, as long as the water doesn't freeze over. The pied-billed grebe's range covers most of eastern and central Canada and all of the United States. In the northern parts of its range, the pied-billed grebe will migrate to areas with open water. It will live year-round In the southern part of its range, as long as the water doesn't freeze over.
Habitat
 The pied-billed grebe can be found in marshes and ponds. It may move to saltwater habitats when freshwater habitats freeze. The pied-billed grebe can be found in marshes and ponds. It may move to saltwater habitats when freshwater habitats freeze.
|
|
Diet
The pied-billed grebe eats mostly aquatic invertebrates, although it will sometimes eat fish, reptiles and amphibians.
Life Cycle
 The male pied-billed grebe or a male and female pair establish a territory during breeding season. Both the male and female gather vegetation from the pond or marsh bottom and build a floating nest in shallow water. The female pied-billed grebe lays 2-10 eggs. Both the male and female incubate the eggs. Incubation takes about 23-27 days. The male pied-billed grebe or a male and female pair establish a territory during breeding season. Both the male and female gather vegetation from the pond or marsh bottom and build a floating nest in shallow water. The female pied-billed grebe lays 2-10 eggs. Both the male and female incubate the eggs. Incubation takes about 23-27 days.
 The chicks are precocial and leave the nest within an hour of hatching. Although they can swim and dive as soon as they leave the nest, the parents protect the chicks and sometimes carry them on their backs. The chicks leave their parents when they are one to two months old. In the southern parts of their range, females may have two broods a year. The chicks are precocial and leave the nest within an hour of hatching. Although they can swim and dive as soon as they leave the nest, the parents protect the chicks and sometimes carry them on their backs. The chicks leave their parents when they are one to two months old. In the southern parts of their range, females may have two broods a year.
Behavior
The pied-billed grebe is an excellent swimmer and diver. It often dives to evade predators. In fact, another name for the pied-billed grebe is the Hell-diver.
|