Characteristics
 The most distinctive characteristic of the roseate spoonbill is its long spoon-shaped bill. It has a white head and chest and light pink wings with a darker pink fringe and very long pink legs. The roseate spoonbill is about two and a half feet in length with a wingspan of about four and a half feet. Both males and females have the same plumage and coloring. The male is slightly larger than the female and its bill is a little longer. The most distinctive characteristic of the roseate spoonbill is its long spoon-shaped bill. It has a white head and chest and light pink wings with a darker pink fringe and very long pink legs. The roseate spoonbill is about two and a half feet in length with a wingspan of about four and a half feet. Both males and females have the same plumage and coloring. The male is slightly larger than the female and its bill is a little longer.
Range
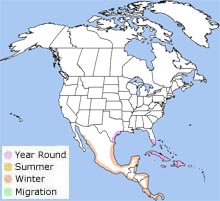 The roseate spoonbill can be found on the coasts of Texas, Louisiana and southern Florida. It is also found in the tropics and in Central and South America. The roseate spoonbill can be found on the coasts of Texas, Louisiana and southern Florida. It is also found in the tropics and in Central and South America.
Habitat
 The roseate spoonbill lives in mangrove swamps, tidal ponds, saltwater lagoons and other areas with brackish water. The roseate spoonbill lives in mangrove swamps, tidal ponds, saltwater lagoons and other areas with brackish water.
Diet
 The roseate spoonbill spends a lot of its time in shallow water feeding. It sweeps its open bill from side to side in the water to sift up food like small fish, shrimp, mollusks, snails and insects. It has touch receptors in its bill that help it feel its prey. Like the flamingo, the roseate spoonbill's pink color comes from the food it eats. Some of the crustaceans it eats feed on algae that give the spoonbill's feathers their rosy pink color. The roseate spoonbill spends a lot of its time in shallow water feeding. It sweeps its open bill from side to side in the water to sift up food like small fish, shrimp, mollusks, snails and insects. It has touch receptors in its bill that help it feel its prey. Like the flamingo, the roseate spoonbill's pink color comes from the food it eats. Some of the crustaceans it eats feed on algae that give the spoonbill's feathers their rosy pink color.
|
|
Life Cycle
 The roseate spoonbill nests in colonies. Males and females pair off for the breeding season and build a nest together. They build large nests of sticks lined with grass and leaves. The nests are built in trees. The female spoonbill lays two to four eggs. Both the female and the male incubate the eggs. The chicks hatch in about three weeks and fledge in around 35 to 42 days. Both the male and female feed the chicks until they are about eight weeks old. Young roseate spoonbills have white feathers with a slight pink tinge on the wings. They don't reach maturity until they are three years old. The roseate spoonbill nests in colonies. Males and females pair off for the breeding season and build a nest together. They build large nests of sticks lined with grass and leaves. The nests are built in trees. The female spoonbill lays two to four eggs. Both the female and the male incubate the eggs. The chicks hatch in about three weeks and fledge in around 35 to 42 days. Both the male and female feed the chicks until they are about eight weeks old. Young roseate spoonbills have white feathers with a slight pink tinge on the wings. They don't reach maturity until they are three years old.
Behavior  Roseate spoonbills are very social. They live in large colonies with other spoonbills, ibises, storks, herons, egrets and cormorants. Roseate spoonbills fly in flocks in long diagonal lines with their legs and neck stretched out. Roseate spoonbills are very social. They live in large colonies with other spoonbills, ibises, storks, herons, egrets and cormorants. Roseate spoonbills fly in flocks in long diagonal lines with their legs and neck stretched out.
 The roseate spoonbill population was once threatened by hunting. In the mid-to-late 1800s its feathers were used in ladies' hats and fans. The population was also threatened by loss of habitat due to drainage and pollution in its habitat. By the early 20th century, the population had shrunk to only a few dozen nesting pairs in the United States. Special protected areas were set aside for them and in the 1940s they were made a protected species. Over time the population recovered and today the roseate spoonbill is no longer a protected species. The roseate spoonbill population was once threatened by hunting. In the mid-to-late 1800s its feathers were used in ladies' hats and fans. The population was also threatened by loss of habitat due to drainage and pollution in its habitat. By the early 20th century, the population had shrunk to only a few dozen nesting pairs in the United States. Special protected areas were set aside for them and in the 1940s they were made a protected species. Over time the population recovered and today the roseate spoonbill is no longer a protected species.
|