Characteristics
 The western meadowlark is about nine inches long. It has a brown and black back and wings and a bright yellow chest with a black V on it. The meadowlark's colors may be a little duller in winter. It has a long pointed bill. The western meadowlark is about nine inches long. It has a brown and black back and wings and a bright yellow chest with a black V on it. The meadowlark's colors may be a little duller in winter. It has a long pointed bill.
The western meadowlark is very similar to the eastern meadowlark. The western meadowlark's yellow color extends a little further onto its cheek. The songs of the two meadowlarks are the easiest way to tell them apart. The song of the western meadowlark is a series of flute-like gurgling notes that go down the scale. The eastern meadowlark's call is a simpler series of whistles.
Range
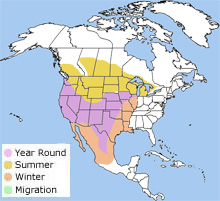 The western meadowlark is a short-distance migrator. Its breeding range stretches from British Columbia, northern Michigan, and northwestern Ohio south to Missouri, central Texas and northern Mexico. The western meadowlark is a short-distance migrator. Its breeding range stretches from British Columbia, northern Michigan, and northwestern Ohio south to Missouri, central Texas and northern Mexico.
Habitat
The western meadowlark lives in meadows, plains, prairies and other open grasslands.
Diet
The meadowlark's diet is mostly insects like caterpillars and grasshoppers, although it will sometimes eat seeds.
|
|
Life Cycle  The male meadow lark uses visual display behaviors to attract a mate. When he finds a female that he wants to mate with, he points his bill in the air, puffs out his yellow throat and flaps his wings above his head. If that doesn't get the female's attention, he hops up and down. The western meadowlark builds its nest on the ground. The female finds a depression in the ground and shapes it by digging in the dirt with her bill. She lines the depression with soft grass and makes a roof by pulling grass and plants over the depression. She then weaves in grass to make a waterproof dome, leaving enough space for an opening. The female lays between three and seven eggs. It takes about 12 days for the eggs to hatch. The meadowlark usually has two broods a year. The male protects the nest by noisily chasing intruders away. The male meadow lark uses visual display behaviors to attract a mate. When he finds a female that he wants to mate with, he points his bill in the air, puffs out his yellow throat and flaps his wings above his head. If that doesn't get the female's attention, he hops up and down. The western meadowlark builds its nest on the ground. The female finds a depression in the ground and shapes it by digging in the dirt with her bill. She lines the depression with soft grass and makes a roof by pulling grass and plants over the depression. She then weaves in grass to make a waterproof dome, leaving enough space for an opening. The female lays between three and seven eggs. It takes about 12 days for the eggs to hatch. The meadowlark usually has two broods a year. The male protects the nest by noisily chasing intruders away.
Behavior
 The male meadowlark arrives at the breeding ground a couple of weeks before the female. It likes to perch on fences, poles and wires to claim and guard its territory. A male's home range is usually about six or seven acres. If another male invades his territory, he may get into a fight with the intruder. Fighting meadowlarks lock their feet together and peck at each other with their beaks. The western meadowlark uses its distinctive song and call to claim territory.. The male meadowlark arrives at the breeding ground a couple of weeks before the female. It likes to perch on fences, poles and wires to claim and guard its territory. A male's home range is usually about six or seven acres. If another male invades his territory, he may get into a fight with the intruder. Fighting meadowlarks lock their feet together and peck at each other with their beaks. The western meadowlark uses its distinctive song and call to claim territory..
|