Description
 The red wolf has gray or black fur mixed with red, especially on its legs and sides. It has a long snout and a long, black-tipped tail. It is larger than a coyote and smaller than a gray wolf. The red wolf weighs between 45-80 pounds and stands about two feet tall from shoulders to feet. It is about four feet long from nose to the tip of its tail. The red wolf has gray or black fur mixed with red, especially on its legs and sides. It has a long snout and a long, black-tipped tail. It is larger than a coyote and smaller than a gray wolf. The red wolf weighs between 45-80 pounds and stands about two feet tall from shoulders to feet. It is about four feet long from nose to the tip of its tail.
Range
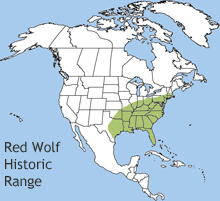 The red wolf once roamed over much of the eastern United States, but by the early 1900s it had disappeared from all states except Texas and Louisiana. The red wolves in those states were mating with coyotes and the population was becoming hybridized. Fearing the species would become extinct, the US Fish and Wildlife Service captured fourteen pure red wolves and started raising them in captivity. The red wolf once roamed over much of the eastern United States, but by the early 1900s it had disappeared from all states except Texas and Louisiana. The red wolves in those states were mating with coyotes and the population was becoming hybridized. Fearing the species would become extinct, the US Fish and Wildlife Service captured fourteen pure red wolves and started raising them in captivity.
 By the 1980s, the red wolf had become extinct in the wild. The first group of captive wolves was released in the Alligator Wildlife Refuge in North Carolina in 1987. The refuge was chosen because it had no coyote population. Today, there are more than 100 red wolves in and around the Alligator River National Wildlife Refuge and Pocosin Lakes National Wildlife Refuge in northeastern North Carolina and over 200 red wolves in captive breeding facilities across the United States. By the 1980s, the red wolf had become extinct in the wild. The first group of captive wolves was released in the Alligator Wildlife Refuge in North Carolina in 1987. The refuge was chosen because it had no coyote population. Today, there are more than 100 red wolves in and around the Alligator River National Wildlife Refuge and Pocosin Lakes National Wildlife Refuge in northeastern North Carolina and over 200 red wolves in captive breeding facilities across the United States.
Habitat
The red wolf makes its home in swamps, forests, and coastal plains. |
|
Diet
 The red wolf is a carnivore. It eats rabbits, birds, rodents and occasionally white-tailed deer. It also eats carrion, or dead animals. The red wolf is a carnivore. It eats rabbits, birds, rodents and occasionally white-tailed deer. It also eats carrion, or dead animals.
Life Cycle
 Red wolves mate from February through March. Two months after mating, the female gives birth to a litter of 2-10 pups. Both the male and the female care for the young. Only the alpha male and alpha female in a pack mate. The alpha male and alpha female are the dominant male and female in a pack. Other wolves in the pack help care for the young and bring food to the female. Red wolves mate from February through March. Two months after mating, the female gives birth to a litter of 2-10 pups. Both the male and the female care for the young. Only the alpha male and alpha female in a pack mate. The alpha male and alpha female are the dominant male and female in a pack. Other wolves in the pack help care for the young and bring food to the female.
Behavior
 The red wolf is mostly nocturnal, although it is sometimes active in the day during the winter months. It makes its den along stream banks in the enlarged burrows of other animals, under tree stumps, or in hollow logs. The red wolf is a social animal and it lives in packs that include a breeding male and female and their pups. Occasionally, there is a second male in the group. Red wolves sometimes form packs to hunt. The red wolf is mostly nocturnal, although it is sometimes active in the day during the winter months. It makes its den along stream banks in the enlarged burrows of other animals, under tree stumps, or in hollow logs. The red wolf is a social animal and it lives in packs that include a breeding male and female and their pups. Occasionally, there is a second male in the group. Red wolves sometimes form packs to hunt.
|