Description  The bullfrog is the largest frog in North America. It is 3-6 inches in length. Females are usually larger than males. Its color can range from light green to dark green to dark brown. Some bullfrogs have patterned bodies, others are solid in color. Its underside is pale yellow or white and may be lightly patterned. It has webbed rear feet and powerful rear legs that help it leap as far as 3-6 feet!
It has large tympanum on the side of its head. The
tympanum is a circular external eardrum. In males, the
tympanum is larger than the bullfrog's eye. In female's it is the same size or smaller than the bullfrog's eyes. The bullfrog does not have dorsolateral ridges.
Dorsolateral ridges are the ridged lines that run down the backs of most species of frogs. The bullfrog is the largest frog in North America. It is 3-6 inches in length. Females are usually larger than males. Its color can range from light green to dark green to dark brown. Some bullfrogs have patterned bodies, others are solid in color. Its underside is pale yellow or white and may be lightly patterned. It has webbed rear feet and powerful rear legs that help it leap as far as 3-6 feet!
It has large tympanum on the side of its head. The
tympanum is a circular external eardrum. In males, the
tympanum is larger than the bullfrog's eye. In female's it is the same size or smaller than the bullfrog's eyes. The bullfrog does not have dorsolateral ridges.
Dorsolateral ridges are the ridged lines that run down the backs of most species of frogs.
Range 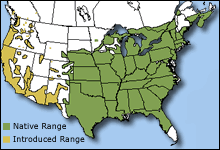 The bullfrog is native to the eastern United States and Canada from Nova Scotia south to Florida and west to Wisconsin and the Great Plains. It has been introduced to parts of the western United States, Europe, Asia, and South America. The bullfrog is native to the eastern United States and Canada from Nova Scotia south to Florida and west to Wisconsin and the Great Plains. It has been introduced to parts of the western United States, Europe, Asia, and South America.
Habitat
 The bullfrog spends most of its time in vegetation at the edge of the water. It is found near ponds, lakes, bogs, rivers, and marshes. The bullfrog spends most of its time in vegetation at the edge of the water. It is found near ponds, lakes, bogs, rivers, and marshes. |
|
Diet
 The bullfrog is an opportunistic feeder. That means it eats just about anything that it can fit into its mouth! It usually waits for its prey to come to it! When a prey animal gets close enough, the bullfrog leaps at it with its mouth wide open! It eats insects, small birds, mammals, fish, snakes, tadpoles, small turtles, crustaceans, and other frogs! Bullfrog tadpoles eat mostly aquatic plants, algae, and aquatic insects. The bullfrog is an opportunistic feeder. That means it eats just about anything that it can fit into its mouth! It usually waits for its prey to come to it! When a prey animal gets close enough, the bullfrog leaps at it with its mouth wide open! It eats insects, small birds, mammals, fish, snakes, tadpoles, small turtles, crustaceans, and other frogs! Bullfrog tadpoles eat mostly aquatic plants, algae, and aquatic insects.
Life Cycle
 Breeding season runs from March through July. The female lays a large, foamy mass of as many as
10,000 to 20,000 eggs on the surface of the water. The male fertilizes the eggs after the female lays them. The tadpoles hatch in about four days. The tadpoles grow to 4-6 inches in length before they change into frogs in one to two years. The longer it takes tadpoles to become a frog, the larger they will be. Bullfrogs can live to be over 10 years old in the wild, but most live 5-6 years. Breeding season runs from March through July. The female lays a large, foamy mass of as many as
10,000 to 20,000 eggs on the surface of the water. The male fertilizes the eggs after the female lays them. The tadpoles hatch in about four days. The tadpoles grow to 4-6 inches in length before they change into frogs in one to two years. The longer it takes tadpoles to become a frog, the larger they will be. Bullfrogs can live to be over 10 years old in the wild, but most live 5-6 years.
Behavior
 The bullfrog gets its name from its deep bull-like call. Bullfrogs are solitary and usually only come together to mate. Male bullfrogs aggressively protect their home range and will often wrestle with an intruding bullfrog!
In the fall, bullfrogs burrow into the mud where they will stay until the spring. In the warmer parts of its range, the bullfrog may be active all year. The bullfrog gets its name from its deep bull-like call. Bullfrogs are solitary and usually only come together to mate. Male bullfrogs aggressively protect their home range and will often wrestle with an intruding bullfrog!
In the fall, bullfrogs burrow into the mud where they will stay until the spring. In the warmer parts of its range, the bullfrog may be active all year.
Video Credit: US Fish and Wildlife |



 The bullfrog is native to the eastern United States and Canada from Nova Scotia south to Florida and west to Wisconsin and the Great Plains. It has been introduced to parts of the western United States, Europe, Asia, and South America.
The bullfrog is native to the eastern United States and Canada from Nova Scotia south to Florida and west to Wisconsin and the Great Plains. It has been introduced to parts of the western United States, Europe, Asia, and South America. 


